Search engine positioning SEO comprises the tactical craft and science of optimising websites to receive higher positions in the search engines’ results pages ( SERPS ). This integrated digital marketing strategy involves combining technical skills, content development, and strategic management to enhance a site’s visibility when users search for it using similar keywords.
The significance of successful Search engine optimisation positioning cannot be overstated in the contemporary digital environment, where 68% of internet use begins with a search engine, and organic search drives 53.3% of overall site traffic. Studies have shown that websites on the first three pages of the search engine results page (SERP) receive 75% of the total clicks, while the remaining websites on the second page account for less than 6% of the total traffic. These statistics are compelling, underscoring the importance of SEO in driving business success and maintaining a strong online presence.
Understanding Search Engine Positioning
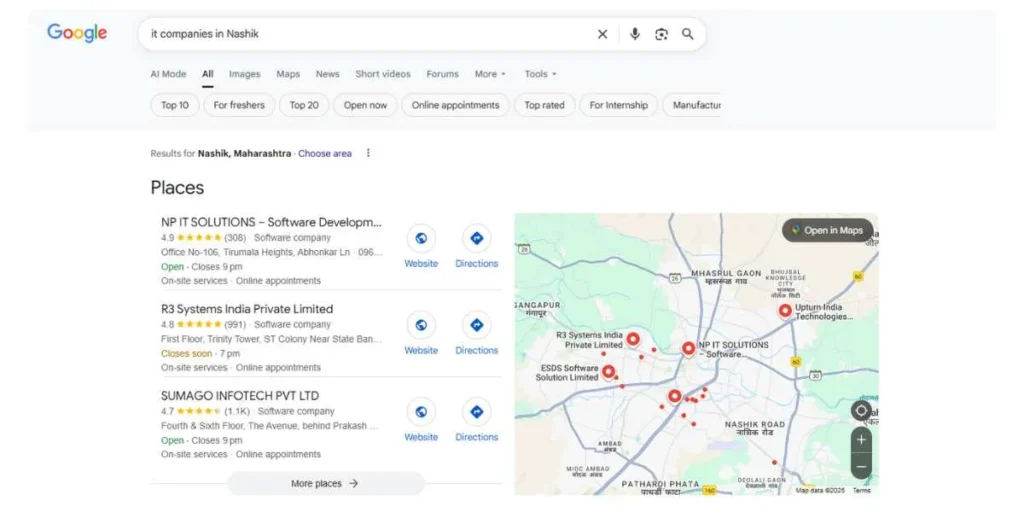
A search engine for SEO is defined as the strategic approach of optimising web pages and websites to enable them to gain the best positions in the search engines whenever they are searching with specific keywords and phrases. This is a complex field that entails understanding how search engines crawl, index, and rank content, as well as adopting specific content strategies to enhance a website’s ranking in organic search results.
Contrary to paid advertising, search engine optimisation SEO is aimed at gaining popularity by being relevant, authoritative, and optimising the user experience. This is done to make websites more discoverable to visitors actively searching for related products, services, or information.
Effective search engine positioning SEO involves a combination of technical optimisation, content strategy, and off-page factors, forming a comprehensive mechanism that ensures search engines rank your website higher for targeted keywords.
How Google and Other Search Engines Determine Ranking Positions
Google’s Ranking Algorithm:
- Crawling and Indexing: Google deploys automated worms, known as crawlers, to focus on and index web pages within the web space. These crawlers crawl the links to gather information on content, formats, and relevance. Crawled pages are then placed in the extensive index, which Google maintains as a library of web materials that can be easily referred to once users use search engines.
- RankBraid and Deep Learning: RankBrain is an AI system at Google that interprets search queries and aligns them with content. This machine learning element evaluates user behavior patterns, including click-through rates, dwell times, and bounce rates, to determine which result best aligns with the user’s intent based on the query.
- Content Relevance Assessment: Google evaluates the relevance of page content to the search query, analyzing the use of keywords, semantic relationships, and topical authority. The algorithm uses not only exact matches on a keyword, but also related terms, synonyms, and context to identify content relevance.
Other Search Engines (Bing, Yahoo, DuckDuckGo):
- Bing Strategy: Bing, a Microsoft product, places a strong emphasis on social metrics, user engagement, and exact match domains. Bing also pays more attention to multimedia content and focuses on existing spheres through regular publishing.
- Yahoo Integration: Yahoo is primarily based on Bing search, incorporating features such as user location and personalisation preferences. Domain age and past performance are also key ranking factors for Yahoo.
- Privacy Focus, DuckDuckGo: This privacy-conscious search engine does not track users and still measures the quality, relevance, and authority of content. DuckDuckGo searches across multiple search engines, maintaining user anonymity throughout the search process.
Key Ranking Factors Influencing Search Positioning
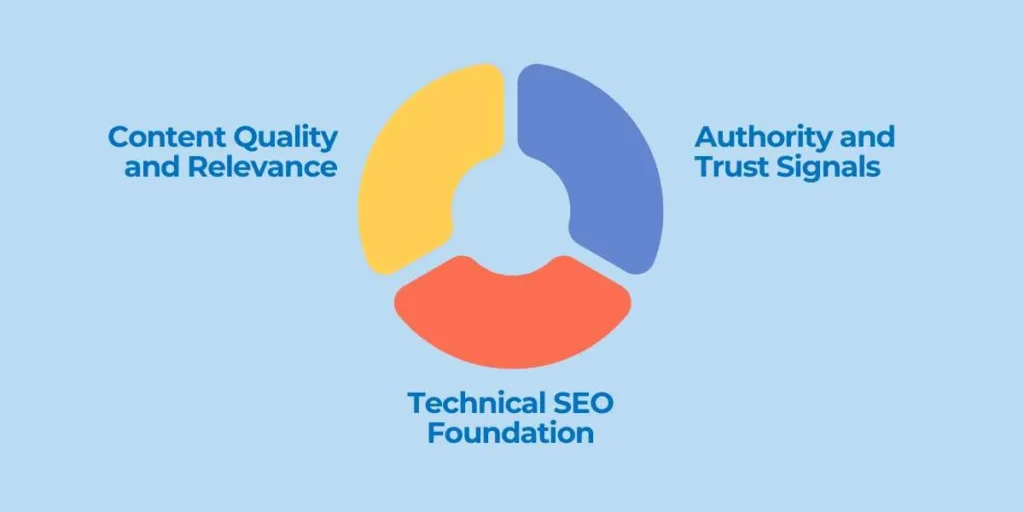
Content Quality and Relevance:
Effective positioning in a search engine through search engine optimisation continues to be based on content. Search engines are flexible towards rich, holistically conducted search content that covers the user’s query exhaustively and delivers actual value to the user.
Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness are key factors in creating high-quality content, which is characterised by correct information, proper referencing, and authoritative sources. The content must align with the user’s search intent, whether they are seeking information, making a purchase, or accessing easy services.
Technical SEO Foundation:
Search engine positioning, or SEO, involves implementing an approach based on technical optimisation. The speed at which pages load greatly influences ranking, as those whose pages load more quickly than slower versions load in less than three seconds. Mobile responsiveness is also critical because increased mobile-first indexing implies that Google relies primarily on mobile variants to rank.
The correct structure of URLs, XML sitemaps, and robots.txt files enables search engine crawling and comprehension of the website’s structure. Several metrics of user experience directly affect the ranking of search engines, including Core Web Vitals metrics such as Largest Contentful Paint, First Input Delay, and Cumulative Layout Shift, among others.
Authority and Trust Signals:
Some of the trust mechanisms and external validation measures used by search engines may determine the authority of a website. High-quality backlinks from reputable sites serve as votes of confidence, indicating that other sites find your information valuable and credible.
Social indicators are not direct ranking factors, but they do show content popularity, which may fuel traffic towards search engine objectives. Even the lack of links with competitors can provide brand mentions that contribute to entity recognition and topical authority. The frequency of publication, authorship, and contact details also helps to build trust.
Core Benefits of Search Engine Positioning
Increased Organic Traffic and Visibility:
Powerful search engine positioning SEO results in highly effective traffic to websites by enhancing rankings through effective placement in search engines, where potential customers are most likely to find relevant information, services, products, or needs. Going up the rankings results in exponentially increased clicks, with the top three positions of rankings absorbing most of the user’s attention and participation.
This gain in visibility has a snowball effect, as even modest SEO efforts result in more engagement indicators, social shares, and earned links, leading to sustainable traffic growth that becomes increasingly cost-effective over time as rankings improve and stabilize.
Cost-Effective Long-term Marketing Investment:
The quality of search engine placement SEO is that it delivers superior profitability compared to traditional advertising means, and the effects of such a strategy are sustainable and cumulative, lasting even after the advertisement campaigns have been terminated. Although establishing initial SEO costs requires time and continuous work, effective positioning builds self-perpetuating traffic generation that continues to generate additional returns over several months or years.
The acquisition cost in terms of organic search generally decreases as the ranking improves, making SEO even more profitable over time. SEO competitive advantages that endure over the long term are principles that make competitors difficult to counter in short time frames, establish market positions, and foster brand agreements that enhance business value in the long term.
Enhanced User Experience and Engagement:
There is a natural rise in the overall user experience that is introduced by the implementation of professional search engine positioning SEO in the form of speed optimisation of websites, their navigation, content structuring, and mobility. This enhancement benefits all site visitors, not just those who arrive through search engines, which drive higher conversion rates and consumer satisfaction.
SEO-balanced materials are typically more detailed and well-structured, providing information that is more relevant to the needs and queries of users. This enhanced user experience provides positive feedback mechanisms, enabling satisfied visitors to anticipate a better chance of returning, sharing content, and becoming customers, thereby contributing to the business’s growth and achieving its SEO objectives.
Types & Pillars of SEO
4 Types of SEO

- On-page SEO: It aims to optimise a single web page in terms of content quality, keyword integration, meta tags, headers, and internal linking structures to enhance search engine rankings and user experiences.
- Off-page SEO involves external forms of SEO, including backlinks, social media marketing, brand mentions, and online reputation management, to establish the site’s authority in search engines.
- Technical SEO: This involves concerns with site structure, including site speed, mobility, crawlability, indexability, security measures, and structured data, to ensure content accessibility and proper processing by search engines.
- Local SEO: Bases its efforts on geographically-focused searches using Google My Business optimisation, regional lists, and local content and management of reviews to acquire local customers and boost local search results.
4 Pillars of SEO
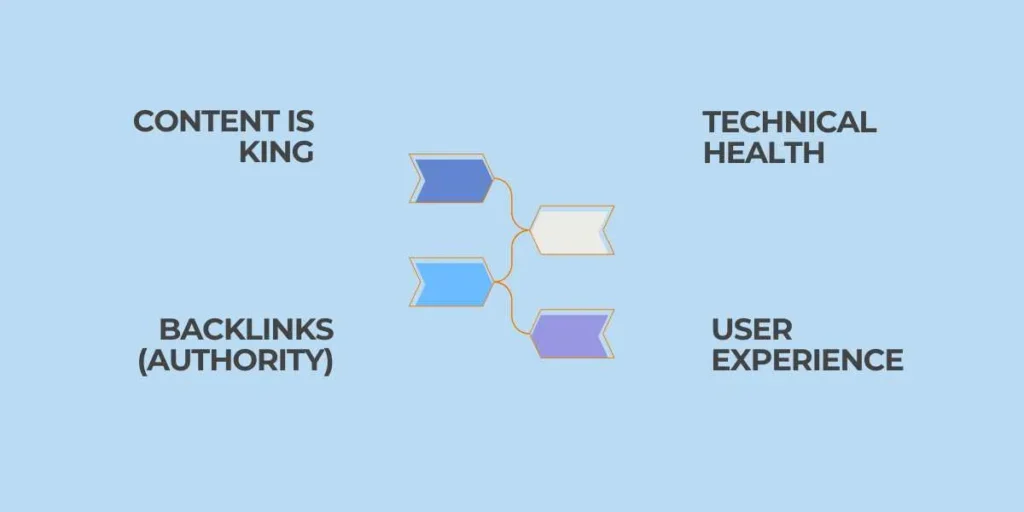
- Content Quality: Valuable, in-depth content that conveys expertise, meets intent, naturally uses appropriate keywords, and also delivers new knowledge or answers to the issues and questions of relevant audiences.
- Technical Health: Well-developed site structure based on high loading speed, mobile readiness, secure links, clean code, correct indexing, and flawless user journey using all gadgets and browsers.
- Backlinks: High-quality and outgoing links to authoritative and relevant sites that communicate trust and credibility to search engines, in addition to generating referral traffic and promoting overall domain authority-building activity.
- User Experience: Easy-to-navigate design, accelerated performance, mobile friendliness, and a pleasant customer experience that engages customers, cross-foams bouncing and leading to repeat visits and conversion.
Search Engine Positioning Techniques
Content Optimisation Techniques
- FAQs: An extensive FAQs section focuses on long-tail keywords, obtains featured snippets, and answers the most common questions of real users to stimulate search.
- Rich Snippets: The structured data markup provides better search results, displaying ratings, price, and other data that tends to have a significant improvement on the click-through rates.
- Long-form Content: Long-form content that exceeds 1,500 words is comprehensive, thoroughly researched, and tailored to meet the requirements of a complex search, which is the primary goal of the user.
Link Building Best Practices
- Relevancy Focus: Target backlinks on industry-aligned websites to maximise link value, ensure topical authorisation, and avoid irrelevant links.
- Diversity Strategy: Develop diverse link profiles on the link texts, types of domains, and link attributes to establish the pattern of natural acquisition.
- Emphasise Authority: Establish authority in high-authority areas with a good reputation to enhance credibility and increase your site’s ranking authority.
Technical Strategies
- Core Web Vitals: Minimise loading speed, loading interactivity, and visual stability indicators to comply with Google’s user experience principles and improve ranking positions.
- HTTPS Security: Utilise SSL certificates across the entire website to ensure secure access, safeguard user information, and support search engine provisions.
- Structured Data: Adding schema markup to the page enhances content visibility for search engines, enabling rich results and optimising specialised search features.
User Engagement Strategies
- Dwell Time Enhancement: Preparative entertaining material, utilising multimedia messages and vivid formatting, can be used to encourage visitors to spend more time viewing pages on websites.
- Reduction of Bouncing: Enhance the loading speed, content relevance, and navigation system structure to retain visitors and encourage them to explore more pages within the site.
- Interactive Content: Utilise videos, infographics, polls, and calculators to increase engagement time, boost social sharing results, and enhance overall user satisfaction indices.
Step-by-Step Guide to Improve SEO Positioning
Step 1: SEO Audit
Conduct a comprehensive website evaluation to identify technical failures, content gaps, and competitive positioning, as well as assess existing performance value, to establish baseline measurements and identify areas for improvement.
Step 2: Keyword Research
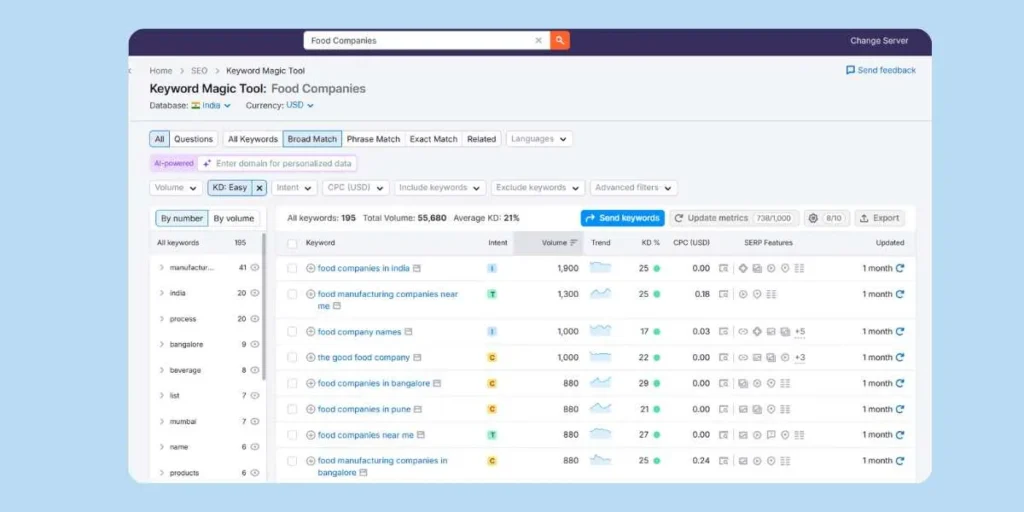
Utilise keyword research tools, such as Google Keyword Planner, to identify keywords based on search volume, competition, and user intent, informing strategic plans for targeted keywords.30
Step 3: On-Page Optimisation
To enhance relevance and understanding for the search engine, minimise title tags, meta descriptions, and headers. Additionally, structure the content, incorporate internal linking, and integrate keywords across the website’s pages.
Step 4: Technical SEO Enhancements
Site speed, mobile responsiveness, crawlability concerns, security implementation, and structured data markup to guarantee a perfect technical basis for placement in the search engine.
Step 5: Off-Page SEO & Backlink Strategy
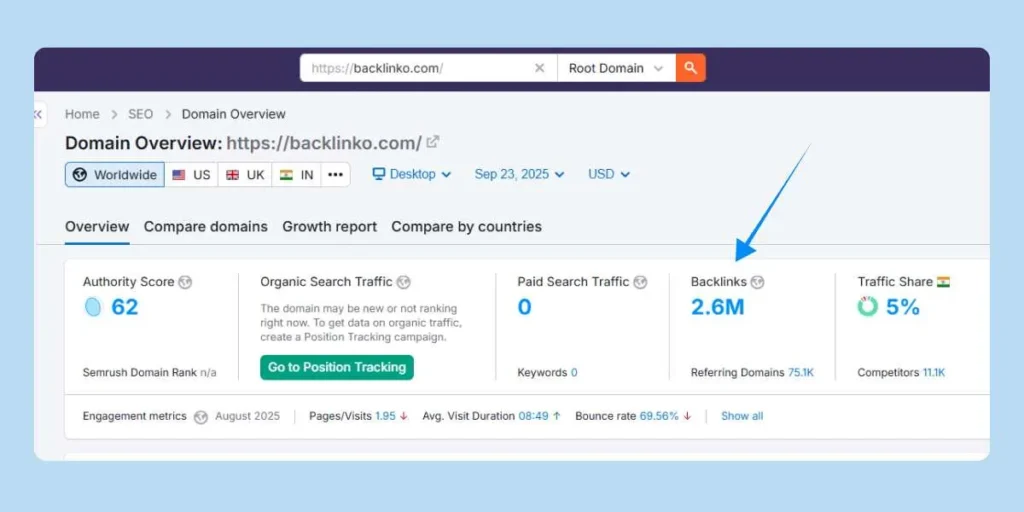
Establish link-building programs, content marketing, and relationship marketing programs to acquire high-quality backlinks and enhance overall site authority signals.
Step 6: Monitor, Analyse & Iterate
Monitor performance indicators, interpret fluctuations in rankings, track competitor actions, and continually refine strategies based on dataset-driven insights and modifications to search algorithms.
Tools & Resources
|
Tool Name |
Purpose |
Tips |
|
Google Search Console | Track traffic sources, user behaviour, conversion metrics, and audience insights | Track traffic sources, user behavior, conversion metrics, and audience insights |
|
Google Analytics | Set up property verification, regularly check coverage reports, and monitor Core Web Vitals. | Configure goal tracking, analyse organic traffic patterns, and monitor bounce rates |
|
SEMrush | Keyword research, competitor analysis, backlink monitoring, site auditing | Keyword research, competitor analysis, backlink monitoring, and site auditing |
|
Ahrefs | Comprehensive SEO analysis, keyword tracking, and tent gap identification | Leverage for content ideation, track referring domains, and analyse SERP features. |
|
Screaming Frog | WordPress SEO optimisation, content analysis, and technical SEO guidance | Crawl sites regularly, identify duplicate content, and analyse meta tag optimisation |
|
Moz | Monitor DA progression, track local rankings, and use MozBar for quick analysis |
Monitor DA progression, track local rankings, use MozBar for quick analysis |
|
PageSpeed Insights | Monitor DA progression, track local rankings, and use MozBar for quick analysis | Comprehensive SEO analysis, keyword tracking, and content gap identification |
|
Yoast SEO | Domain authority tracking, local SEO management, and rank tracking |
Configure properly, use readability analysis, optimize for focus keywords |
Advanced Tips for Page-Level Ranking
- Semantic Keyword Inclusion: Add semantically related words and long-tail derivations throughout the entire content in the same way as missing primary keywords are placed to reflect the topical authority and cover a wide variety of search terms. Search with latent semantic indexing (LSI) keywords, where we utilise keywords that support the main topics without incurring the penalty of key stuffing.
- Vanity of Snippet Optimisation: Draft writing in a way that will rank in featured snippets with a specific structure by having clear headings, list and bullet employment, and secondary question and answer writing. Organise the content into convenient portions that the search engine can select as the top search engine results.
- Internal Connectivity Architecture: Develop a strategic internal connection to link systems, sharing page authority across your site and with your audience. Accommodate descriptive anchor text and include links to other descriptive text of value that supports overall site authority.
- Freshness Signals: Utilise Freshness Signals to regularly update outdated information on the duplicate content with new facts, figures, and knowledge, ensuring it remains relevant and valuable. Search engines prefer new, up-to-date content to represent the modern trends in the industry and the demand of the consumers.
- User Intent Alignment: Predict the intent behind specific keywords and ensure the content meets the user’s exact needs. Regardless of whether it is informational, transactional, or navigational, content must meet the purpose behind search queries.
- Mobile-First Optimisation: Determine the mobile-first indexing approach and create and optimise content for that audience, as mobile users are considered first. Make loading times competitive, navigation easy, and ensure viewpoints are optimised for smaller screens to improve your competitive search ranking.
Common SEO Mistakes That Hurt Positioning
- Keyword Stuffing and Over-Optimisation: Excessive keyword repetition can lead to an unnatural point, resulting in a poor user experience and potentially causing a search engine penalty. Pay attention to natural language and user value instead of an arbitrarily known very low delinquent target keyword density.
- Disregard Technical SEO Foundations: Failing to address site speed, mobile-friendliness, and search engine crawling issues renders other attempts to improve search ineffective. Technical problems prevent search engines from accessing and recognising the content of websites correctly, regardless of whether the content is good or bad.
- Poor Google Backlink Acquisition: Search Penalties can be used to counteract the intrusion of poor-quality, spammy, or irrelevant backlinks, which can have severe effects on search ranking. Work on receiving genuine links from relevant, authoritative sources through valuable content.
- Copycat Content Problems: Having the same or more similar content on multiple pages can be problematic for Google, as it can lead to wasted search rank. Ensure that the information on every page is engaging and that related content can be canonicalised appropriately as needed.
- Failure to use User Experience Metrics: Overlooking the bounced rate, dwell time and interference to determine the quality and relevance of the piece of content to users. These measures are becoming increasingly used by search engines to evaluate the effectiveness and user satisfaction with content.
- Mixed Strategic Implementation in SEO: Periodic optimisation and unstable strategies do not guarantee long-term success. SEO requires a long-term, regular application of best practices to achieve lasting results and implement ongoing improvements.
Conclusion
The art of search engine positioning SEO cannot be achieved without the complex knowledge of technical optimisation, content, and user experience principles. It is a complex field that requires patience, consistency, and ongoing education, as the search algorithm advances and user preferences evolve. Effective search engine placement SEO helps build long-term competitive advantages by creating high levels of organic visibility, generating traffic efficiently and at low costs, and increasing user interaction levels.
The tactics and methods presented in this guide are the basic elements of a successful immediate and future digital marketing strategy, helping to increase website rankings and achieve success in digital marketing. Do not forget that successful SEO positioning on search engines is a continuous process that should be monitored, analysed, and adjusted with changes that will help sustain and enhance its performance. Websites that prioritise delivering value to users over technical best practices in their pursuit of business growth and success on the Internet can achieve and sustain high rankings in search engines.
FAQs
What does it mean by search engine positioning SEO?
Search engine positioning SEO refers to the art of positioning web pages at a higher ranking in the result list of search engines by means of technical, content, and authority-building techniques applied to web pages.
How to enhance the SEO positioning of a website?
Advance SEO placement by conducting comprehensive audits, keyword analysis, on-page optimisation, technical optimisation, developing high-quality content, and maintaining consistent link-building activities, all while ensuring continuous monitoring and improvement.
What can be mentioned as search engine positioning?
These include advocating for the first page in relation to the keywords that we believe our target audience may be using, visible featured sniping, search local pack implementation in location-related searches, and image/video search availability.
What is the difference between search engine positioning and SEO?
SEO is a collective term, and search engine positioning refers to the process of achieving and maintaining high positions on search engine results pages through optimisation.
What is the time taken to rank a page at Google?
New improvements in ranking usually require 3-6 months, and the improvement of competitive keywords may take 6-12 months or longer, depending on the level of competition, authority, and quality of optimisation.
What software are you going to use to track that search engine?
Research/Tool: PopSearch engines include Google Search Console, SEMrush, Ahrefs, Moz, SERPWatcher, and AccuRanker, which are among the most popular position trackers used by buyers to monitor their positions in searches and rankings.
