As businesses upgrade their technology, the secure disposal of outdated IT assets has become a critical responsibility. Improper IT asset disposal (ITAD) poses significant risks to both data security and environmental sustainability.
Unsecured data can lead to breaches and legal consequences, while improper disposal contributes to the global e-waste crisis. This article will explore the importance of a formal ITAD program and outline best practices for balancing data protection with sustainability.
The Importance of a Formal IT Asset Disposition (ITAD) Program
IT Asset Disposition (ITAD) refers to the process of managing, securing, and disposing of a company’s outdated or unused IT equipment. This includes everything from computers and laptops to servers and networking devices. ITAD plays a crucial role in a company’s overall IT lifecycle management, ensuring that assets are disposed of securely and sustainably while maximizing their value.
Having a formal ITAD program in place is becoming increasingly important. It helps businesses to:
- Prevent data breaches by ensuring sensitive information is securely erased before disposal.
- Mitigate risks associated with improper disposal, such as environmental damage or non-compliance with regulations.
- Support compliance with industry regulations, including data protection laws like GDPR and HIPAA.
A well-structured ITAD program provides businesses with legal protection, reduces operational risks, and preserves company reputation by demonstrating a commitment to responsible data management and sustainability.
Ensuring Data Security During Disposal
When disposing of IT assets, data security is the highest priority. Ensuring that sensitive information is completely erased is crucial to preventing data breaches and protecting company’s privacy.
Certified data wiping is the most effective method to securely erase data from devices. Standards like DoD 5220.22-M, NIST 800-88, and GDPR compliance outline the specific processes for securely wiping hard drives and other storage devices. These standards ensure that all data is permanently removed, making recovery impossible.
Choosing a certified IT asset disposal company for data destruction ensures that the process is thorough and compliant with legal requirements. Trusted companies combine secure disposal methods with data loss prevention tools to safeguard sensitive information, follow industry best practices, and provide certificates of destruction for proper documentation.
Choosing a certified IT Asset disposal company for data destruction ensures that the process is thorough and compliant with legal requirements. Trusted companies follow industry best practices and provide certificates of destruction for documentation.
For businesses with large volumes of assets, cloud-based data destruction and certified third-party services offer scalable and secure solutions. These services provide efficient data wiping and destruction while ensuring compliance with privacy regulations.
Environmental Considerations: E-Waste Recycling Certifications
The responsible disposal of electronic waste, or e-waste, is essential to minimize environmental harm. Improper recycling of IT assets can lead to hazardous chemicals leaching into the environment, polluting soil and water. To avoid these risks, it’s crucial for businesses to partner with certified e-waste recyclers who follow stringent environmental standards.
R2 and e-Stewards certifications are two widely recognized benchmarks for responsible e-waste recycling. These certifications ensure that recyclers:
Follow sustainable IT practices for environmental protection, such as safely handling hazardous materials and reducing emissions. Prioritize worker safety, ensuring that the disposal process does not endanger those involved in recycling operations.
By choosing certified recyclers, businesses help reduce landfill waste, as these programs emphasize reusing and recycling electronic components instead of discarding them. The positive environmental impact is significant, contributing to the reduction of e-waste and the promotion of a circular economy.
Options for Extending Device Life
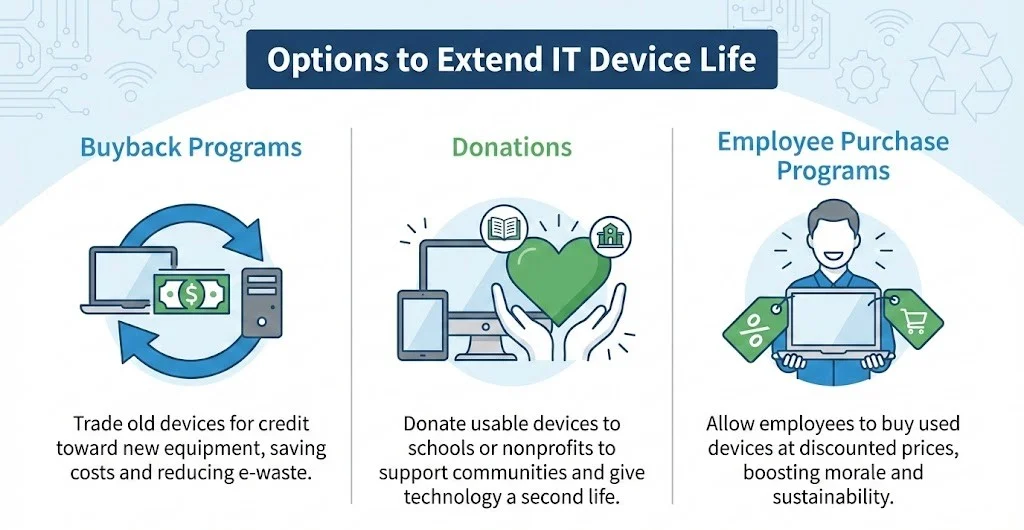
Extending the life of IT devices not only saves money but also helps reduce e-waste. Here are some practical options businesses can consider:
Buyback Programs
Buyback programs allow businesses to sell or trade in old equipment for credit toward new devices. Many manufacturers and resellers offer buyback deals, allowing companies to recoup some of their initial investment while upgrading to newer technologies.
Benefits:
- Cost savings by offsetting the price of new equipment.
- Extended device utility, keeping older devices in use longer.
- Reducing e-waste by giving devices a second life.
Donations
Another option is to donate old devices to non-profits, educational institutions, or charitable organizations. By donating equipment, businesses can support community initiatives and provide access to technology for those in need.
Benefits:
- Contributing to social responsibility and community development.
- Giving old devices a new purpose, rather than discarding them.
Employee Purchase Programs
Employee purchase programs offer staff the opportunity to buy used devices at discounted prices when they are retired from company use. This option helps employees acquire affordable technology while promoting sustainability.
Benefits:
- Incentivizes employees by providing affordable tech options.
- Boosts employee morale and creates a sense of value.
- Encourages recycling and keeping devices in use within the workforce.
These strategies allow businesses to maximize the value of their IT assets, reduce environmental impact, and promote positive relationships with employees and the community.
Creating an IT Asset Disposal Policy
An effective IT asset disposal policy is essential for ensuring the secure, compliant, and environmentally responsible disposal of outdated hardware. This policy should address the entire lifecycle of IT assets, from procurement to final disposal, ensuring that all necessary steps are taken to protect sensitive data and meet legal and environmental standards. Key elements of the policy are:
Documentation of the Lifecycle
The policy should include clear documentation for each step in the asset’s lifecycle, from procurement through usage, to eventual disposal. This ensures that every device is tracked and handled properly throughout its life within the organization.
Compliance with Relevant Standards and Regulations
Adhering to industry regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and other local data protection laws, is critical. The policy must specify compliance with these standards for data privacy and security during disposal, ensuring that all required steps are followed to avoid penalties.
Tracking the Disposal Process
A secure disposal process should include tracking mechanisms for each asset, including documentation of data destruction. This can involve keeping records of when and how data was erased, who was responsible, and when the asset was finally disposed of or recycled.
Steps to Ensure a Seamless and Secure Disposition Process
To ensure that IT asset disposal is secure and seamless, businesses should take the following steps:
- Collaboration Between Departments: Involve the IT, legal, and compliance teams to create a unified approach to asset disposal. The IT department ensures secure data destruction, while the legal and compliance teams ensure adherence to laws and regulations.
- Third-Party Vendor Management: If third-party vendors are involved in the disposal process, ensure that they follow the same rigorous standards outlined in the policy. Establish clear vendor agreements and audit processes to monitor compliance.
Creating Policies with Audit Trails for Accountability
Incorporating audit trails into the IT asset disposal policy is essential for accountability. These trails document every stage of the disposal process, from data destruction to final disposal, and help ensure compliance with legal and company standards. Having a well-documented audit trail provides transparency and serves as a valuable reference during internal audits or legal reviews.
Overcoming Common IT Asset Disposal Challenges

While IT asset disposal is a crucial part of managing end-of-life technology, businesses often face a range of challenges that can complicate the process. Here are some common challenges businesses encounter and strategies to overcome them:
1. Lack of Standardized Processes
Many businesses lack a standardized process for IT asset disposal, which can lead to inconsistencies, missed steps, and potential security risks. Without a clear procedure, assets may be disposed of in an unstructured way, increasing the likelihood of errors.
Solution:
Establish a clearly defined IT asset disposal policy that outlines every step from procurement to disposal. Include specific guidelines on tracking, data destruction, compliance, and sustainable disposal. This policy should be communicated across the organization to ensure consistent and secure handling of all IT assets.
2. Difficulties in Tracking and Auditing
As organizations accumulate large quantities of IT assets over time, keeping track of all devices and ensuring they are properly disposed of can become a logistical challenge. The lack of an efficient tracking system can lead to lost devices and gaps in compliance.
Solution:
Implement a centralized asset management system that tracks each device throughout its lifecycle. This system should log key information such as asset type, location, condition, and disposal status. Pair this with audit trails to document all actions taken during the disposal process, ensuring accountability and transparency.
3. Resistance to Recycling or Disposal
Some employees or departments may resist recycling or disposing of old equipment due to concerns over cost, inconvenience, or perceived loss of value. This can result in cluttered storage and delays in proper asset disposal.
Solution:
Promote a culture of sustainability by educating employees on the importance of proper asset disposal and the environmental impact of e-waste. Offer incentives, such as employee purchase programs for used equipment or buyback programs, to make the process more appealing and accessible.
4. Insufficient Vendor Coordination
Coordinating with third-party vendors for asset disposal, data destruction, and recycling can be challenging, especially when working with multiple vendors across different regions. Inconsistent communication and service levels can lead to delays or security risks.
Solution:
Work with trusted and certified vendors who provide comprehensive services and can handle all aspects of IT asset disposal, from data destruction to recycling. Establish clear contracts and service level agreements (SLAs) that outline expectations for performance, timelines, and reporting.
5. Balancing Disposal Costs with Security and Compliance
Many businesses face the challenge of balancing the cost of disposal with the need for secure and compliant methods. While options like drive shredding and certified data wiping are highly secure, they can be costly, especially for organizations with many devices to dispose of.
Solution:
Consider a tiered disposal approach where high-risk devices, such as those with sensitive data, undergo the most secure (and costly) disposal methods, while lower-risk devices are wiped and resold or recycled. Also, explore cost-effective options like trade-in programs with manufacturers, which can help offset the cost of secure disposal.
Conclusion
Businesses must strike a careful balance between data security and environmental sustainability when managing IT Asset Disposal. Ensuring that sensitive data is securely destroyed is crucial for protecting the organization’s reputation and complying with privacy regulations. At the same time, responsible e-waste management is essential to reducing environmental impact and contributing to a more sustainable future.

